Indeed, relays tend to switch from one state to another much quicker than big mechanical 3PDT switches, which causes the "pop" noises to appear. The gainier the pedal, the more it will amplify the pop and make it louder.
So I adapted a system that I have found on Stompville that suppresses all these noises. Here is the result, with a (very) simple "before and after" video:
Works well!
Beware: before reading this post, I strongly suggest that you read my post about relay bypass to understand well what relay bypass and microprocessors are about.
How does it work?
It is quite simple: when the pedal is switched on, the sound is mute to get rid of the pop!The signal will be send to ground while the relay is switching. Then, when the pop has disappeared, the pedal is "unmuted" and the pedal is on. There will be a small period of 40 ms of silence, but do not worry, in practice, you really cant tell!
In order to mute the pedal during the switching, we are going to use a photoFET.
Ok, but what is a photoFET?
It is a small component that looks like a mini 4-pins IC, which include a LED and a switch made by 2 MOSFET that will let the current flow when the LED is on. It is kind of a switch activated by a current, with on / off positions.

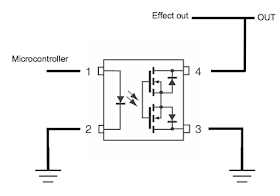
When the microcontroller does not activates the LED: the current cannot flow between the pins 3 and 4 of the photoFET and the signal can go out.
Basically, we got a mute switch here!
So... Why don't we use a photoFET to switch the signal instead of using a noisy relay?
PhotoFET are smaller, they use less current and are virtually indestructible (non mechanical)! However, there is one downside with photoFETs: they use MOSFETs that modify your tone! Indeed, active photoFETs have a low resistance (2 Ohms), but a quite high capacitance (130 pF). If you have read my post about cables, you know that 130 pF represents almost 3 meters of a good cable! This is not very good for a "true bypass" system!
Here, it is not a problem as we only use it to mute the signal, but for a bypass signal, that would be quite awful for instance.
Here is the schematic of this "relay bypass version 2":
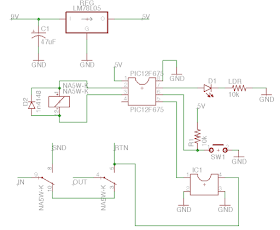
Thus, it is almost exactly the same circuit as the relay bypass circuit, except that the photoFET is connected to the pin 5 of the microcontroller, and the pin 4 of the microcontroller is connected to the end of the effect circuit.
I choose to use a TLP222A photoFET, which is easy to find, and not that expensive.
How to code it?
We will use the pin number 5 of the PIC to activate the LED of the photoFET.Beware: pin numer 4 (GPIO3) is an "input only" pin, so we cannot use it to activate the LED. You must use the pin number 5!
Do not worry, we will find a use for the pin number 4 later...
Lets open MPLab to create the header, that will be exactly the same as the one we made before in the relay bypass blog post. Create a new project for the PIC12F675, and add a header file with the following configuration:
// CONFIG
#pragma config FOSC = INTRCIO // Internal clock of the PIC is on
#pragma config WDTE = OFF // Watchdog Timer disabled
#pragma config PWRTE = OFF // Power-Up Timer disabled
#pragma config MCLRE = OFF // GP3/MCLR pin is a GPIO
#pragma config BOREN = OFF // Brown-out Detect disabled
#pragma config CP = OFF // No code protection
#pragma config CPD = OFF // No internal memory protection
// Defines the internal oscillator / clock frequency (4MHz)
#define _XTAL_FREQ 4000000
#pragma config FOSC = INTRCIO // Internal clock of the PIC is on
#pragma config WDTE = OFF // Watchdog Timer disabled
#pragma config PWRTE = OFF // Power-Up Timer disabled
#pragma config MCLRE = OFF // GP3/MCLR pin is a GPIO
#pragma config BOREN = OFF // Brown-out Detect disabled
#pragma config CP = OFF // No code protection
#pragma config CPD = OFF // No internal memory protection
// Defines the internal oscillator / clock frequency (4MHz)
#define _XTAL_FREQ 4000000
If you do not remember exactly what is the role of all these parts, read my relay bypass article.
Lets switch for the code now! We have to add a sequence when the effect is going to change its state (on or off), with 4 steps:
- Turn on the photoFET: signal goes to ground
- Activate the relay : the "pop" noise goes to ground through the photoFET
- Wait a bit until the "pop" is completely gone
- Turn off the photoFET
To do that, we will use a variable "changestate" that will tell the microcontroller when to change state, that we will define at the beginning of the code by writing:
uint8_t changestate; // changement d'état (pour couper le son avec le photoFET)
changestate=0;
changestate=0;
Initially, the value is 0. When the value of changestate is 1, the microcontroller will change the state of the pedal (on to off or off to on)
On lui donne la valeur de zéro initialement. Lorsque la valeur de changestate sera de 1, le microcontrolleur activera la pédale.
For instance, changestate will be equal to 1 when the switch is engaged (with debouncing):
if(GP1 == 0) { // if the switch is pressed
__delay_ms(15); // debounce
if(GP1 == 0) {
__delay_ms(200); // switch is off
if(GP1 == 1) {
changestate = 1; // changestate = 1
}
else {
changestate = 0;
}
}
}
__delay_ms(10);
}
__delay_ms(15); // debounce
if(GP1 == 0) {
__delay_ms(200); // switch is off
if(GP1 == 1) {
changestate = 1; // changestate = 1
}
else {
changestate = 0;
}
}
}
__delay_ms(10);
}
Then, we will have to precise the 4 steps we have defined earlier in the code when changestate is equal to 1, depending on the state of the pedal. If the pedal is on (state =1), it is turned off, and if it is off (state = 1), the effect is turned on:
if(changestate == 1) {
__delay_ms(20);
if(state == 0) { // if the pedal is off
GP2 = 1; // activates the photoFET (step 1)
__delay_ms(10);
GP0 = 1; // LED on
GP5 = 1; // relay on (step 2)
GP4 = 0;
__delay_ms(30); // wait for the pop to go to ground (step 3)
GP2 = 0; // photoFET off (step 4)
state = 1; } // pedal is on
else { // if the pedal is on, same steps
GP2 = 1;
__delay_ms(10);
GP0 = 0; // LED off
GP5 = 0; // relay off
GP4 = 0;
__delay_ms(30);
GP2 = 0;
state = 0;
}
__delay_ms(20);
changestate=0; // reset changestate to 0 (otherwise it will switch continuously)
}
if (state == 1) { // effect on
GP0 = 1; // LED on
GP5 = 1; // relay on
GP4 = 0; }
else { // effect off
GP0 = 0; // LED off
GP5 = 0; // relay off
GP4 = 0;
}
__delay_ms(20);
if(state == 0) { // if the pedal is off
GP2 = 1; // activates the photoFET (step 1)
__delay_ms(10);
GP0 = 1; // LED on
GP5 = 1; // relay on (step 2)
GP4 = 0;
__delay_ms(30); // wait for the pop to go to ground (step 3)
GP2 = 0; // photoFET off (step 4)
state = 1; } // pedal is on
else { // if the pedal is on, same steps
GP2 = 1;
__delay_ms(10);
GP0 = 0; // LED off
GP5 = 0; // relay off
GP4 = 0;
__delay_ms(30);
GP2 = 0;
state = 0;
}
__delay_ms(20);
changestate=0; // reset changestate to 0 (otherwise it will switch continuously)
}
if (state == 1) { // effect on
GP0 = 1; // LED on
GP5 = 1; // relay on
GP4 = 0; }
else { // effect off
GP0 = 0; // LED off
GP5 = 0; // relay off
GP4 = 0;
}
It adds a small delay during activation of the effect (40ms), but while playing, you cannot tell at all. However, there is no more "pop" noise, which is completely audible!
It works really well, and we only need to add one component! Finally, we have a true bypass system that is reliable, with clickless switches and absolutely silent!
Here is the full code. Do not hesitate to read again the relay bypass post to understand which part does what.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <xc.h>
#include "header.h"
void main(void) {
ANSEL = 0; // No analog GPIOs
CMCON = 0x07; // comparator off
ADCON0 = 0; // AD ND converter off
TRISIO0 = 0; // output LED
TRISIO1 = 1; // input footswtich
TRISIO2 = 0; // output TGP222A photo FET
TRISIO5 = 0; // output activated relay
TRISIO4 = 0; // output ground connection of the relay
GPIO = 0; // set outputs as low level (0V)
uint8_t state; // set the on or off state of the pedal
state=0; // pedal off at the beginning
uint8_t changestate; // changing state
changestate=0;
while(1) { // main loop
if(GP1 == 0) { // if the switch is activated
__delay_ms(15);
if(GP1 == 0) {
__delay_ms(200);
if(GP1 == 1) {
changestate = 1;
}
else {
changestate = 0;
}
}
}
__delay_ms(10);
}
if(changestate == 1) {
__delay_ms(20);
if(state == 0) { // change to on
GP2 = 1; // PhotoFET on
__delay_ms(10);
GP0 = 1; // LED on
GP5 = 1; // relay on
GP4 = 0;
__delay_ms(30);
GP2 = 0; // PhotoFET off
state = 1; }
else { // change to off
GP2 = 1;
__delay_ms(10);
GP0 = 0; // LED off
GP5 = 0; // relay off
GP4 = 0;
__delay_ms(40);
GP2 = 0;
state = 0;
}
__delay_ms(20);
changestate=0;
}
if (state == 1) { // effect on
GP0 = 1; // LED on
GP5 = 1; // relay on
GP4 = 0; }
else { // effect off
GP0 = 0; // LED off
GP5 = 0; // relay off
GP4 = 0;
}
}
__delay_ms(10);
}
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <xc.h>
#include "header.h"
void main(void) {
ANSEL = 0; // No analog GPIOs
CMCON = 0x07; // comparator off
ADCON0 = 0; // AD ND converter off
TRISIO0 = 0; // output LED
TRISIO1 = 1; // input footswtich
TRISIO2 = 0; // output TGP222A photo FET
TRISIO5 = 0; // output activated relay
TRISIO4 = 0; // output ground connection of the relay
GPIO = 0; // set outputs as low level (0V)
uint8_t state; // set the on or off state of the pedal
state=0; // pedal off at the beginning
uint8_t changestate; // changing state
changestate=0;
while(1) { // main loop
if(GP1 == 0) { // if the switch is activated
__delay_ms(15);
if(GP1 == 0) {
__delay_ms(200);
if(GP1 == 1) {
changestate = 1;
}
else {
changestate = 0;
}
}
}
__delay_ms(10);
}
if(changestate == 1) {
__delay_ms(20);
if(state == 0) { // change to on
GP2 = 1; // PhotoFET on
__delay_ms(10);
GP0 = 1; // LED on
GP5 = 1; // relay on
GP4 = 0;
__delay_ms(30);
GP2 = 0; // PhotoFET off
state = 1; }
else { // change to off
GP2 = 1;
__delay_ms(10);
GP0 = 0; // LED off
GP5 = 0; // relay off
GP4 = 0;
__delay_ms(40);
GP2 = 0;
state = 0;
}
__delay_ms(20);
changestate=0;
}
if (state == 1) { // effect on
GP0 = 1; // LED on
GP5 = 1; // relay on
GP4 = 0; }
else { // effect off
GP0 = 0; // LED off
GP5 = 0; // relay off
GP4 = 0;
}
}
__delay_ms(10);
}
There it is! I hope that everything is clear. I know it is not an easy subject, but guess what? You can ask any question you like in the comment section!
In a next blog post, we will see how to add a "temporary mode" like in my Montagne Tremolo!
If you liked this post, thank me by liking the Coda Effects Facebook Page!
To go further
Stompville post that helped me a lot!Datasheet of the TLP222A

I have one here with 40106 IC. It would be interesting to try and make this one work, to avoid programming the PIC.
ReplyDeletevery interesting article, have to "convert" it to my AVR attiny chip and give it a go... thanks for sharing
ReplyDeleteAbsolutely silent is NOT when input signal is still present.
ReplyDeleteI could not get this to work. My first attempt, the pedal/LED would turn on but not off. I erased the PIC and started again and now nothing works and the only way I can get the relay to change states is by jumping pins one and two of the 12F675. Also, if I enter the complete code as listed (copy/paste or line by line) I get an error and the code can't be compiled. The culprit seems to be the double closed brackets after GP4=; -
ReplyDeleteGP4 = 0;
}
}
__delay_ms(10);
}
If I leave both of the brackets in the code, I get an error. If I remove the second bracket, the code compiles but the PIC does not change the relay state. Any suggestions? Thanks.
I have the same problem. Has anyone solved it? Thanks.
DeleteHello!
DeleteMaybe try to use the new version of my relay bypass system: http://www.coda-effects.com/2017/02/relay-bypass-final-code.html
Also, the problem might comes from the fact that the PIC cannot deliver enough current to make the relay switch. A way to make it happen is to add a transistor before the relay to increase the amount of current provided to the relay.
Hey How are you??? Do you recommend to dedicate a pin of the PIC for the Relay ground?? Or can i take the Relay ground directly to the PCB Ground?? I order a bunch of Relays but it will take a long to arrive and i can not make tests, Greeting from MExico!!! and sorry for the english :O
ReplyDeleteActually, I have never tried this option, could be interesting! Let me know if it works like this.
Deletework well excellent system .... is possible made it with Attiny 13A and H11F1 or H11F3 ?
ReplyDeleteCould be! The H11F1 has a fairly low capacitance when on so it seems very doable to me. However, the code will be different as it is Arduino and not a PIC.
Deleteany chance that a different model of the photocell works? the ones ive found of those you stated are expensive where ive found them :(
ReplyDeleteHi, I made on a few of these relay bypasses with your stuff and installed them in many boss pedals. My issue now is, I have an SD-2 which has a bicolor LED related to the two channels on the pedal. How do I wire the anode side to the relay bypass module if there are two anodes? They seem to run through additional subcircuits and I cant find where to tap both of them to the relay bypass.
ReplyDeleteHeres a schematic of the sd-2
https://s1.postimg.org/8cx8yp5c3v/Boss_SD2_schematic.jpg
Heres the same schematic closer up on the LED section
https://s1.postimg.org/8cx8yp5c3v/Boss_SD2_schematic.jpg
https://s1.postimg.org/66h9luk26n/led_circuit.jpg sorry i posted two of the same image. Heres the led section close up
Deletehttps://s1.postimg.org/66h9luk26n/led_circuit.jpg
Hi there Benoit,
ReplyDeleteThere are some parts you can consider changing. First off, you could use the built in weak pulldown resistor (WPU) and thus there is no need for R1. However, if the relay switch is used in a daisy chain there is a possibility of ground loop which will make the relay react erratic. For this you could use a 100nF between both pins of the switch.
Second, why do you keep the last codeblock (if (state == 1) {.... delay_ms(10)})? It is redundant as far as I can see.
PS I designed a similar switch with a latch/momentary option and multicolor LED and also found the article from stompville. Thumbs up to you and stompville.
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeletesuper helpful post!
ReplyDeletehowever, i think i spotted one error.
the capacitance of the photofet (Coff = 130 pF) applies to the off-state, meaning it will be there all the time, except when it is muting the signal.
however, it is still a fairly low value. if you are concerned though, you could get the TPL222G, which has a Coff rating of 30 pF.
Is it an idea to put a 10pf in series between ground and pin 3 of the photofet? That would reduce it to about 10pF (1/130+1/10=1/Cv -> Cv=9,28pf)
ReplyDeleteI don't understand how that would help. Yet I can picture an added value of let's say 130 pF an analogue to the the guitar tone knob.
ReplyDeleteA common tone capacitor runs at 22000 pf (with the knob fully turned). Replace that cap with a 130 pF one. I doubt you would hear a difference.
What about using a CPC1017N. Ron:16 Ohm and Coff:25pf... Also, the switching speeds are 10ms (both...time on and time off)
ReplyDeleteThere is another candidate, the CPC1008 With Ron:8Ohm and Coff: 6pf... But much faster...about 1-2 ms
Hi. Very interesting post
ReplyDeleteWhy did you use a photoFET instead of two regular MOSFETs? is there any difference?
I think this works only because you are not playng. If you activate it while a low note is playing you would hear a click. It will be actually caused by the antipop system itself
ReplyDeleteGreat guide for the great bypass! The only ambiguos part left is what's the purpose of 1n4148 in parallel with relay power pins?
ReplyDeleteHi!!!! Why you didn't use resistor before first pin tlp222a, you conected the LED on output pin? The pin gives 5 volts??? its not dangerous for TLP222 or PIC12???
ReplyDelete