
It is quite in good shape for a 50 years old guitar pedal! The pots allowed me to date it, from 1966. There is a serial number as well, but I do not really know how they work. I think each serial correspond to the number of the unit. Thus, the lower the serial, the older the pedal is. This fuzz is not that big for a vintage fuzz, especially compared to the 1973 Supa Tonebender that I had on my bench before.
At the front of the pedal, there are two controls: Volume and Attack (translate by "Fuzz"). It is the second version of the Fuzz-tone, the FZ1-A. The two knobs are also original, and are the same "reflector" knobs used on vintage Les Paul.

Indeed, the pedal was made by Gibson in the same factory as the Les Pauls, in Kalamazoo, Michigan! Thus, a lot of parts are shared with vintage Les Pauls: the knobs, potentiometers and some low value capacitors. I believe that it allowed Gibson to lower a bit their prices, selling this pedal for $40 at the time (which should be around $300 today though...). Gibson even included it in some bass produced at that time, like the Gibson EB-0F, Gibson EB-SF 1250 and Epiphone Newport EB-SF!
Inside, the circuit is dead-simple. Three pnp transistors, wire on an eyelet bakelite board create the saturation. They are Motorola 2n2614, old germanium transistors. The original FZ1 used germanium 1n270 transistors, whereas the FZ1-A version used Motorola 2n2614. It has also old carbon-comp resistors, from the sixties!
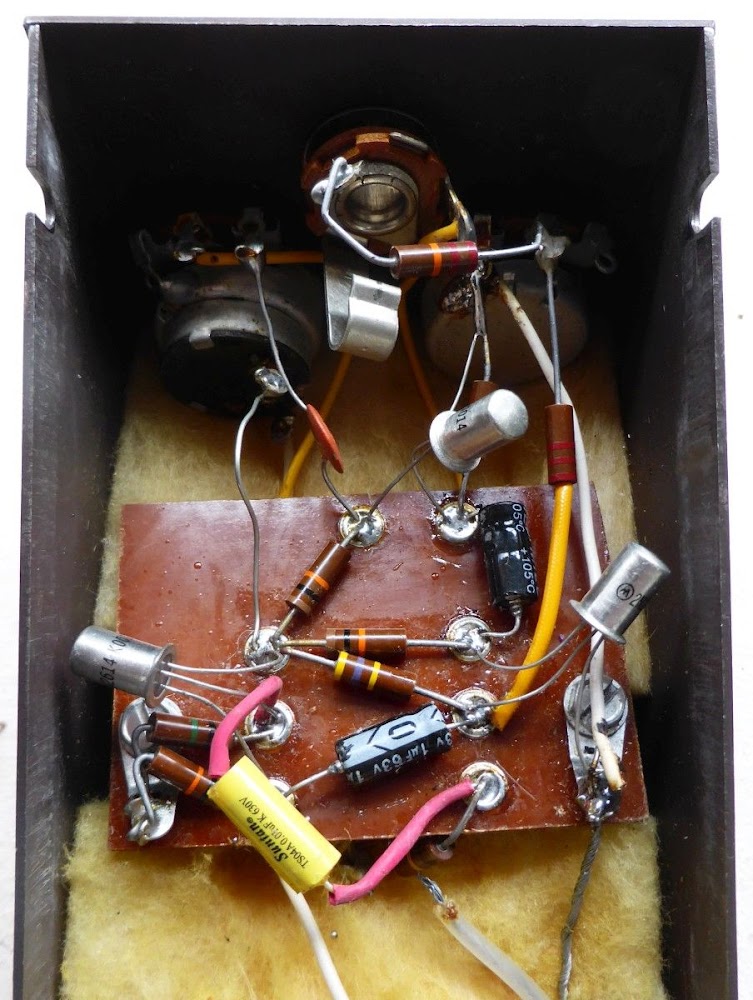

The electrolytic capacitors had been replaced (very common, old electrolytic transistors tend to leak, and are often replaced in vintage builds like this one), the yellow Suntan capacitor is not original as well. Apart from that, all the rest is original! It feels quite extraordinary to discover a perfectly preserved circuit like this one when opening the pedal, it feels a bit like opening Toutankhamon's tumb!
Close up on one of the transistors:

The fuzz has only one input, and a jack allows you to connect it directly to your amp. Well, it is one the first guitar pedals, so pedalboard were not really an option at that time!
History of the Maestro Fuzz-Tone
The Maestro Fuzz-Tone FZ1 was the first fuzz pedal ever! In the early 50s, blues guitarists started to push their amps to make it distort and create a weird, unusual guitar sound: saturated guitar sound. Some players even made holes in the speaker to make the distortion even greater! In 1961, Grady Martin bought a faulty transformer creating a weird distortion, and recorded a song called "The Fuzz" with it. The name "Fuzz" was born!The song became really famous, and many artists did want to use the same sound. However, the transformer died shortly after the song was recorded. Glenn Snody, the original owner of the transformer and Revis Hobbs, a radio engineer, wanted to recreate the sound of the transformer using transistors. And this is how the Fuzz-Tone circuit was created! Snody and Hobbs showed it to Gibson, who developed a prototype and commercialized a first batch of 5000 units in 1962, selling it for retail price of $40 at the time.
The original Fuzz-Tone advertisement is quite amusing, they say it can sounds like an organ or mellow woodwinds... I would rather say: a huge screaming dirty nasty sound that will crush your ears lol! Here is the record:
I do not know how they made the recording, I cannot reproduce any of these sounds at home! This record feels like listening to the really birth of rock...
The Fuzz-Tone was quite a commercial failure: besides the 5000 units shipped in 1962, Gibson did not sell any other fuzz pedal until 1965! Indeed, in 1965, the Rolling Stones issued "Satisfaction". Keith Richards did use the FZ1 on the records to make the main riff. It was used to emulate the sound of a horn, because the Stones did not have horns in their band at the time.
The Fuzz-Tone became then really famous (the hype for guitar effects was already there :) ), and Gibson sold more than 40 000 units later! It also inspired many other manufacturers that begin to create other fuzz circuits like the Tonebender, Fuzz Face...etc.
Versions and other models
The FZ1 was declined in several models. The FZ1 was quite a commercial failure, and Gibson did not make more of them... It is also the more collectible version fo the FZ-1, as only around 5000 units were manufactured (less than the Klon Centaur!). You can distinguish between these four version by looking at the front of the enclosure. Here are the four main versions of the FZ1 (spot the differences!):
In 1965, the Rolling Stones made it famous, and Gibson issued another model, the FZ1-A. It did not use the same transistors (2n2614 instead of the original 2n270), and used only one AA battery!
There was a few change to the circuit: the two 20uF coupling electrolytic capacitors were replaced by 1uF ones, and the second collector resistor was changed to 10k instead of 1.5k, maybe to compensate the lower voltage. The name of the model is clearly written on the front of the enclosure, with "FZ-1A" instead of "FZ-1".
It was first manufactured in the Kalamazoo factory in Michigan, and then, after 1968 (not so sure about the exact date though), FZ1-A were later manufactured in Lincolnwood, Illinois. The location of the factory is written below the Gibson logo. The serial numbers are also higher (see below).
Finally, the FZ1-A was a reissue in 2002, exactly reproducing the circuit and the enclosure, with the same transistors! Fortunately for us, it was manufactured in Nashville, Tennessee, which is written just below the Gibson logo. Also, the reissues do not have a serial number engraved.
The FZ1 also had successors. Later on, Maestro issued the FZ1-B, which uses silicon transistors. The circuit is thus quite different, powered by a 9V battery, and the Fuzz does not sound quite the same. It is less saturated, and a bit buzzy. It is pictured on the left here:

Later on, the FZ1-S model was issued in a huge enclosure, with a very cool looking metallic circle. It has three controls, and a switch for the tone control: you have guessed it, it has almost nothing to do with the original Fuzz Tone! It is closer to a Fender Blender or an Univox Super Fuzz (no octave though).
Serial numbers of the FZ1: date your pedal easily
Sometimes pots have been replaced, and the pedal can be hard to date. I tried to decipher the year of each serial number. This is not an official statement, however, I have emailed Gibson about it, maybe they have more infos to give me. In the meantime, if you are the lucky owner of a FZ1, you can give me the serial number and the date of your pedal. Thus, we can complete the table!| Model | Year | Factory | Units shipped | Min-Max serial seen |
Serial between ? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FZ1 | 1962 | Kalamazoo, Michigan | 5461 | 870-4628 | 1-5461 |
| FZ1-A | 1965 | Kalamazoo, Michigan | 3454 | 6174-? | 5462-8916 |
| 1966 | Kalamazoo, Michigan | 20943 | 10665-21354 | 8917-29860 | |
| 1967 | Kalamazoo, Michigan | 6625 | 22933 | 29861-36485 | |
| 1968 | Kalamazoo, Michigan | ? | 42970 | 36486-42970 | |
| FZ1-A | Lincolnwood, Illinois | ? | 43762-44537 | 43762-44537 | |
| FZ1-B | Lincolnwood, Illinois | ? | No serial number | no serial | |
| FZ1-A Reissue | 2002 | Nashville, Tennessee | ? | No serial number | no serial |
- Find the name of the model (FZ1 or FZ1-A?)
- Find the place it was made (Kalamazoo, Lincolnwood or Nashville?)
- Read the serial number
- If your pedal is not in the serial numbers indicated above, open it and look at the potentiometers. The date should be on it, like on vintage guitars.
Circuit analysis: how does it work?
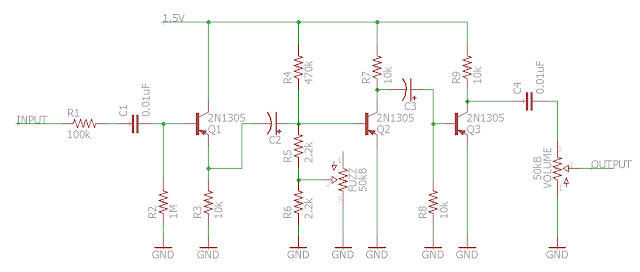
As mentioned before, the circuit is based around three transistors:Like usual, let's divide it in functional parts:
It has a negative polarity because of the PNP transistors, and use only one AA battery, so 1.5V only!
Input stage
The input stage is basically a small buffer that also cuts some bass.
First, there is a coupling capacitor of 0.01uF. It avoid parasitic DC current to enter the circuit, and also filter some low frequencies: you loose a bit of bass. A 1M resistor connected to ground prevents noises when the pedal is switched on.
The first transistor is wired in emitter follower (not really common in guitar pedals), in order to adapt the impedance of the guitar signal. The emitter is indeed connected directly to the power supply. Thus, it has a gain of around unity, and does not amplify the signal.
There is another electrolytic coupling capacitor after this capacitor.
Saturation stage
This is where the fuzz happens! A transistor is pushed beyond its limits and saturates because of the gain that it too high.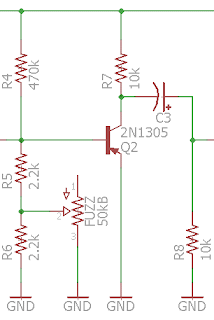
Basically, there is too much current going to Q2, which creates saturation: the fuzz is there!
Note that the emitter of the transistor is wired directly to ground to make the gain of Q2 maximum! 10k is also quite a high value for the collector resistor, and it helps increasing the saturation even more. If you replace it by a bigger value, you can increase the saturation even more!
C3 is a coupling capacitor that prevents any parasitic current from the collector to go in the circuit.
Output stage
This stage amplifies the signal and can even boost it a bit to get a nice volume output.
It is very simple : the Q3 transistor amplifies the signal a lot (and saturates as well : there is no emitter resistor, plus a high value collector resistor = very high gain!).
The C4 capacitor is a coupling capacitor that prevents parasitic DC current to go out. C4 also cuts some bass, as it is quite a low value (10nF). If you use a bigger value, the pedal will be more bassy and muddy. I actually like it with a higher value, it really changes the character of the fuzz.
Finally, a volume knob sends more or less signal to ground. If you turn the potentiometer to the right, the resistance increase, and more signal goes out the circuit instead of going to ground: higher volume output! It is the same control that is used in the Fuzz Face.
There it is! I hope that this post was helpful and fun to read! If you have any remark or question, post a comment below!
If you liked this post, thank me by linking Coda Effects Facebook Page! You can also follow Coda Effects on Instagram and Twitter.
To go further
- Vintage guitar magazine article about the FZ1. Great sum up of the history of the pedal.
- FZ1 webpage on the Effects Database
- Great sum up of all the schematics of the FZ1 by David Morin
- Original Fuzz-Tone patent from 1962 (and its version on google patents)
- Smallbear Electronics post about the Fuzz-Tone
- Wikipedia webpage of the Fuzz Tone


6 Comment
As always, bravo!!!! "very common, old electrolytic transistors tend to leak" check misspelling.
AnswerGreat, thanks a lot!
AnswerIt's a father of Tone Bender MK1 and they are very close to each other. But I've noticed that the TB mk1 doesn't like high output pickups. It's overloading with this. But with the FZ-1A no problem at all.
Strange thing for me because I can't find the difference between them which determines it's different behavior with hi output guitars.
Sorry about two pedals comparison in the one theme about the one FZ1-A
volume control should be a 500k reverse audio
AnswerR6 should be 22k,at least in every schematic i've seen
AnswerCan you simply reverse the electrolytic caps and wire hot battery to jack n make it a germanium NPN? Circuit o have stock of military glass cv7112 gold for fuzz m boosters etc..nic article ,loneing for that splatty fuzztone older I am had 2 63 ones n sold or traded ions back..now I'm recording n need once in while
AnswerSorry to tell you, but the FZ1A uses 2N2613, 2N2614 by RCA. Not Motorolas. It appears you have a model that’s been “worked on”.. not entirely original.
Answer